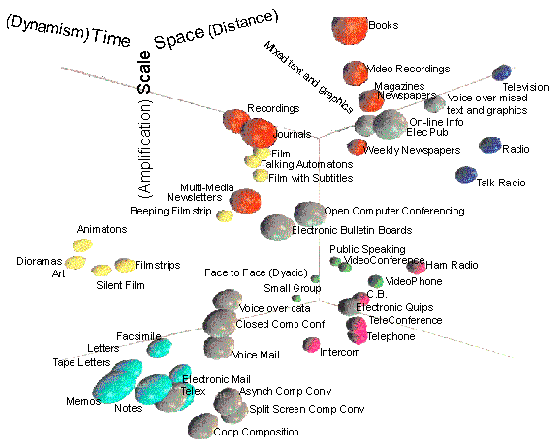
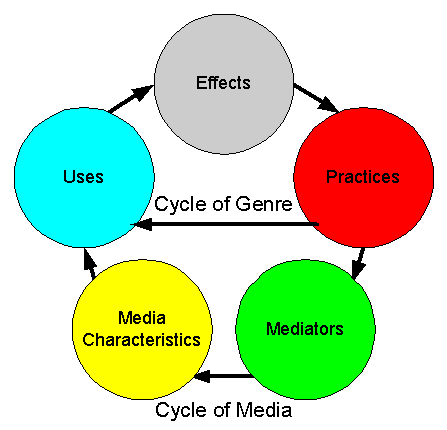
Time Relationship
|
Pre-Internet Media
|
Internet Media
|
Delinearization
|
Correspondence, Newspapers
|
On-line Databases, Listservs, Newsgroups
|
Relinearization
|
Drama, Shopping Lists
|
Agent relinearized Listservs and Newsgroups
|
Desequencing
|
|
Chat, Instant Messenger
|
Resequencing
|
|
E-Mail, Computer Conferencings, Autothreaded Messaging, Voice into
Text Concurrent Interaction
|
Hyperlinearity
|
|
Web Sites, Task-Oriented UI
|
Metalinearity
|
|
Wiki Collaborative Composition, Structured Conferencing
|
Synchrony
|
Face to Face Interaction and Telephone
|
Shared Whiteboards, Shared Desktops, Internet Telephone and Videophone
|
Asynchrony
|
Letters, Art, Recorded Music, Film, Books
|
E-Mail, Computer Conferencing
|
Near-Synchrony
|
|
Instant Messenger, Asynchronous Telephone
|
Supersynchony
|
|
Supersynchronous Interaction, Synchronous Media Use Ecologies
|
Serial Creation
|
Television, Music, Theatre, and Film
|
Groupware
|
Indexing
|
Reference Books, Text Books
|
On-Line Databases, E-Mail, Computer Conferencing
|
Reference Pointers
|
Bird Books
|
E-Mail, Computer Conferencing, Hypermedia Documents, Relational Databases
|